How Form Encoding Works
by Joe Marshall on August 24th, 2021

Forms are a fundamental building block of the web - one of the most atomic units of data collection on the internet.
When they send information to the server, they do so using one of three encodings (specified using the <form> attribute enctype):
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
This type represents a URL encoded form and is the default value if the enctype attribute is not set. URL encoding means - unsurprisingly - that the data from the form is being sent to the server by being appended to the current URL.
Code
<form enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
<input type="text" name="email" value="joe@formcake.com" />
<input type="text" name="name" value="joe" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>Request
This will end up creating a GET request (the default form HTTP request type) that looks like:
https://example.org?email=joe%40formcake.com&name=joeNotice that the @ symbol is being URL encoded as %40.
multipart/form-data
The multipart form encoding type is used primarily for sending information about files (so a form with <input type="file" />).
Code
<form
enctype="multipart/form-data"
method="POST"
action="https://example.org/wmqfte/file/agent/AGENT1@QM1/webuploads"
>
<input type="file" name="resume" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>Request
Opening the code in my browser, I attach a copy of my resume and click Submit. Going into the devtools I can see my POST request and, in the body of it, my encoded file, which is correctly being read as a PDF.
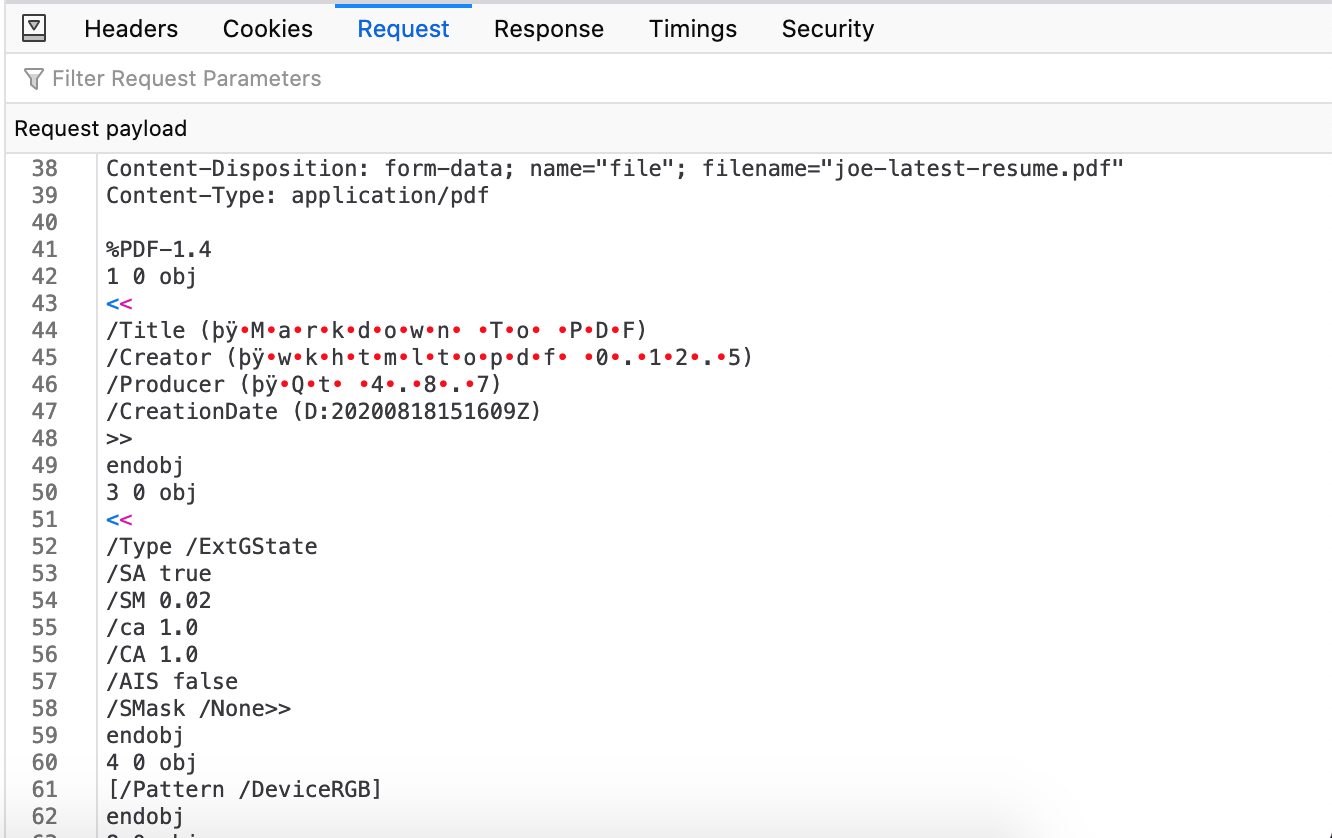
Boundary
There's also an extra field you'll notice in the request's Content-Type, boundary. Boundary can either be passed by you or will be set as a default in the data and is, simply put, a delimiter that will be used to separate the different parts of your multipart form data.
text/plain
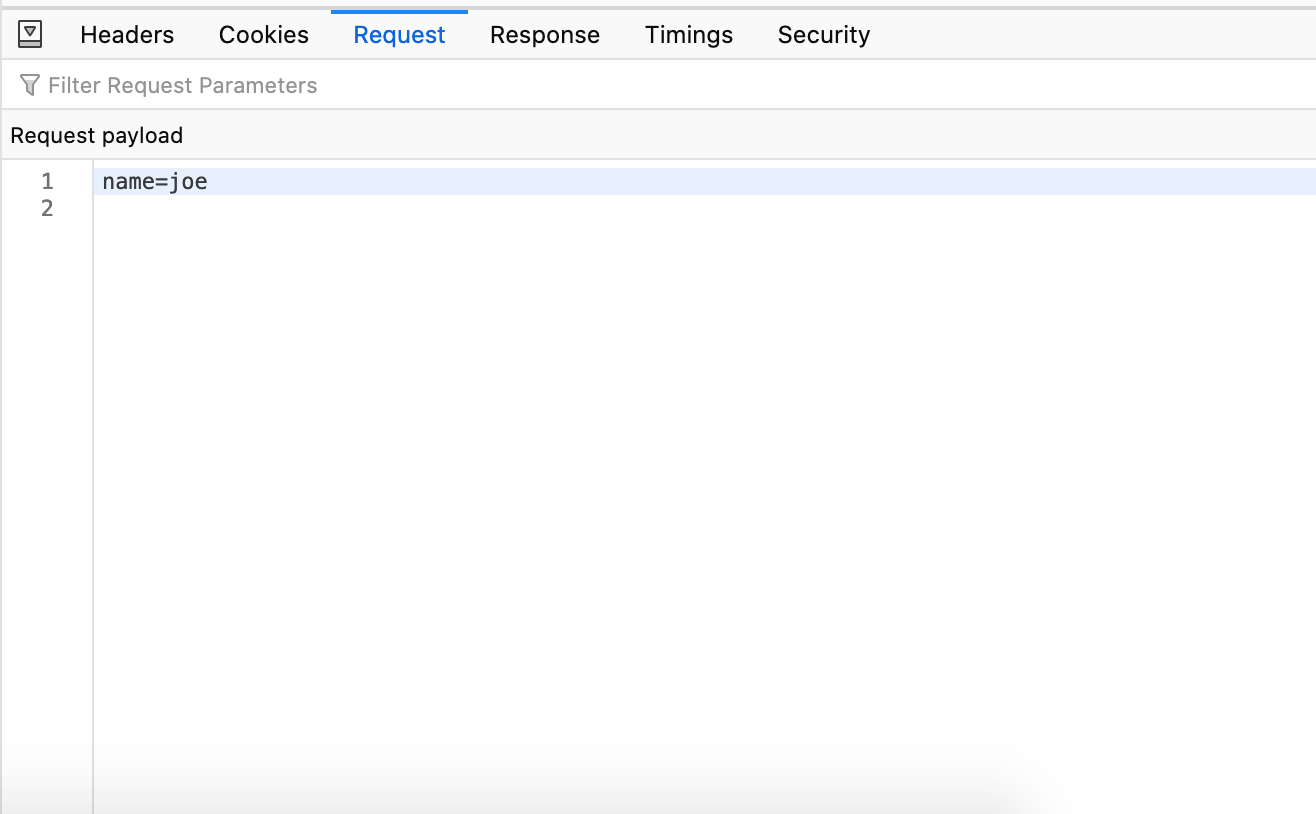
This was introduced by HTML5 for debugging purposes. A form with this type sends plain text data just like the name implies.
Code
<form enctype="text/plain">
<input type="text" name="name" value="joe" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>Request
No surprises here, we just get a simple key=value pairing.
Some Extra Quirks
As the MDN Web Docs explain, the enctype can be overriden by "formenctype attributes on <button>, <input type="submit">, or <input type="image">" so make sure to be aware of that when editing an existing form.
Also, if the value of the method attribute is POST, then the enctype is the MIME type of the form submission. The MIME Type is a media-type two-part identifier for file formats and other information transmitted through the Internet. An example of a MIME type would be application/json - or for that matter, our very own application/x-www-form-urlencoded, which we've already covered.
Hopefully this short primer has given you a greater understanding of how form submissions on the web are transmitted. It's just one of a series explaining the ins and outs of forms on the web. Sign up below for notifications!